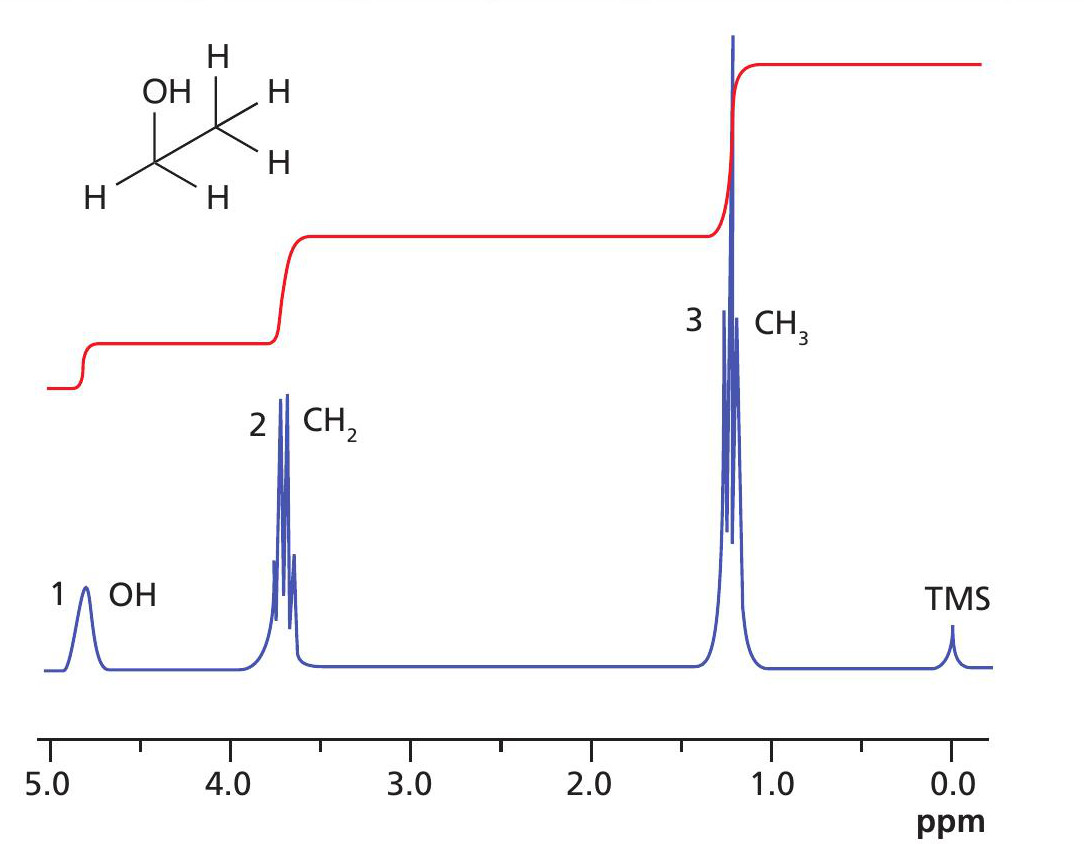
Figure 1 1H NMR spectrum of ethanol. The numbers by the peaks correspond to their integral ratios
In your chemistry course you are likely to be asked to interpret spectra presented to you. If you go on to study chemistry at university, you will probably use NMR spectra to check your laboratory skills by confirming the identity of compounds you have synthesised in the lab.
Let’s begin with an example. If we insert a sample of ethanol
Your organisation does not have access to this article.
Sign up today to give your students the edge they need to achieve their best grades with subject expertise
Subscribe




