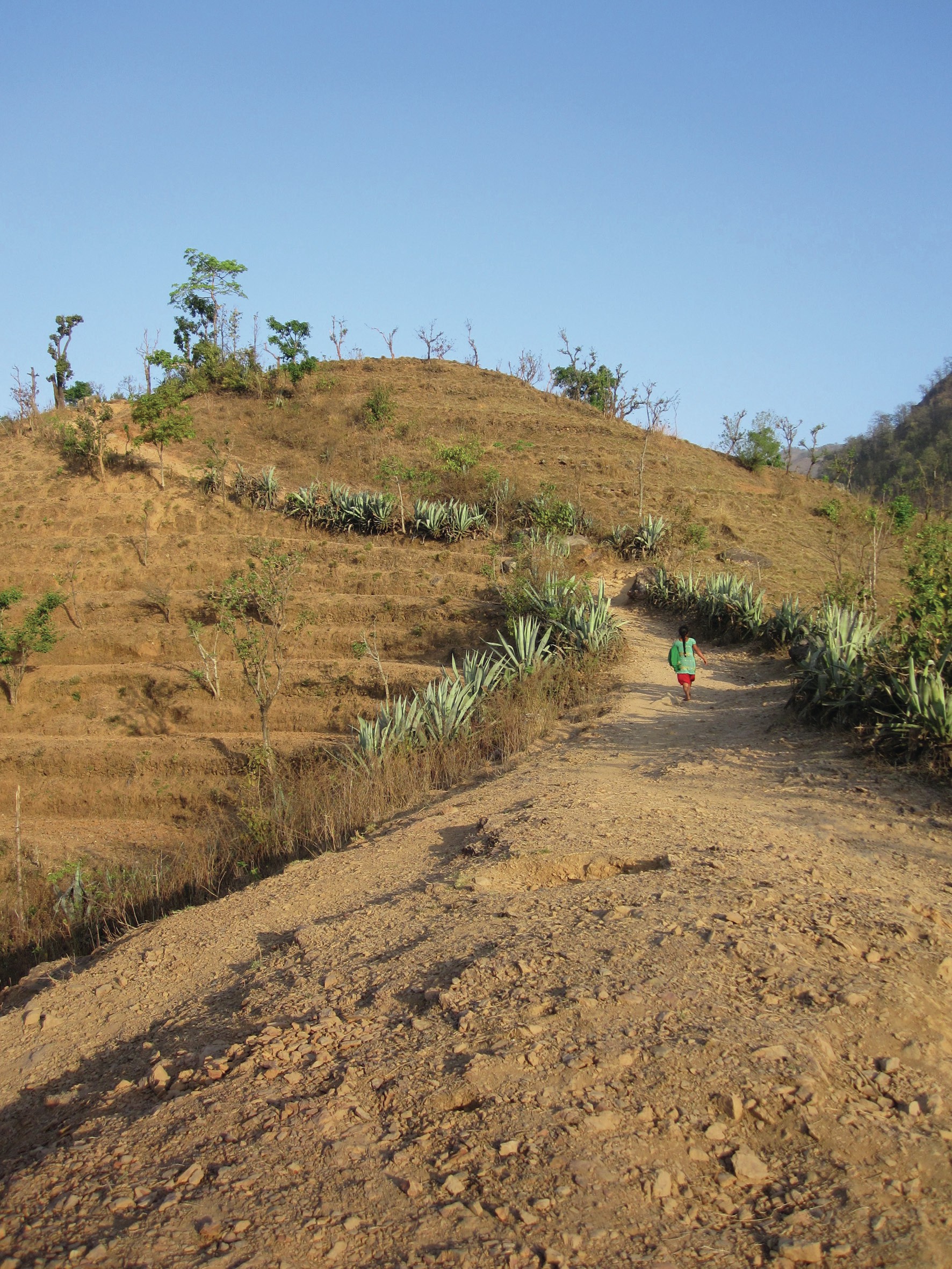
Nepal is one of the poorest countries in the world. Most of its population lives below the international poverty line. Because the country is so poor, people are vulnerable to environmental hazards such as drought, flooding and landslides. Agriculture is an important sector of the economy and supports much of the rural population. Poverty is worse in rural areas, where it is hard for communities to adapt to the lack of environmental resources such as water. But environmental conditions in rural areas have been badly affected by national growth and development, social and political governance, and climate change.
Water is the most vital environmental resource in Nepal and water reserves are replenished by the annual monsoon. More than 80% of rain falls during summer (June–September) and this provides good conditions for crop production and hydroelectric power (HEP) generation. (Nepal relies on HEP for most of its power.) However, these immense deluges of rain also result in environmental hazards such as flash flooding, landslides and soil erosion.
Your organisation does not have access to this article.
Sign up today to give your students the edge they need to achieve their best grades with subject expertise
Subscribe